The possible role of tolerant strains in excluding metals from the host plant is discussed. Bacillaris isolates and 14 of A.
Two species that are different in their copper sensitivity are the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and yellow perch Perca flavescens.

. Samples were taken of plants growing in waste from a copper mine and from nearby areas just outside the mine. A Explain how different subspecies of giraffe may have evolved from a common ancestor. We explicitly compared acute.
Cerevisiae evolution of copper tolerance is associated with the increase of antioxidative activities as already documented by others and with a reduced production of ROS. Quitensis against copper is governed by the described mechanisms for metal-tolerant species we analyze the accumulation of GSH and PCs. 2a bWhen cucumber plants were grown at higher pHs ie.
On the contrary non-evolved cells suffer severe oxidative stress as showed. For both species the. The results showing that GSH and PC 2-PC 5 are accumulated with significant differences with the control in copper treated plants Fig.
Up to 24 cash back Samples were taken of plants growing in waste from a copper mine and from nearby areas just outside the mine. Two species that are different in their copper sensitivity are the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and yellow perch Perca flavescens. Agrostis tenuis and Dactylis glomerata produced fully copper tolerant survivors at a frequency of 008 per cent.
There were however signifi-cant differences between individuals within popu-lations in tolerance of all four metals Table 3. For both species the. Bacillaris seem more tolerant to copper compared to the others intraspecific variations exist.
We suppose that ectomycorrhizal fungi are submitted to a selection for metal tolerance in polluted soils. A Explain how natural selection could produce a copper-tolerant population in the mine. The mean copper tolerance of plants from the mine waste was found to be four times higher than that of plants in the surrounding area.
In an investigation the tolerance to copper ions of the grass Agrostis tenuis was determined. Explain how this might eventually lead to the production of a new species of Agrostis. More than 20 of the St.
The mean copper tolerance of plants from the mine waste was found to be four times higher than that of plants in the surrounding area. Specifically we investigated heat cold and desiccation resistance after acclimatization to. Two species that are different in their copper sensitivity are the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and yellow perch Perca flavescens.
Up to 10 cash back A simple model is developed to explain this discrepancy in which the determining factor is not the rate of spread but the maximum response achievable under the two contrasting models of polygenic or major gene inheritance. Two species that are different in their copper sensitivity are the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and yellow perch Perca flavescens. Google Scholar Crow J.
And copper Cu tolerance are completely different since zinc tolerance does not result in copper tolerance and vice versa. We explicitly compared acute toxicity median lethal concentrations via 96-h LC50s and whole-body Na loss in both organisms in two distinct water chemistries ie hard and soft water. 60 and 75 the intermediate Cu concentration.
We explicitly compared acute toxicity median lethal concentrations via 96h LC50s and wholebody Na loss in both organisms in two distinct water chemistries ie hard and soft water. We explicitly compared acute toxicity median lethal concentrations via 96-h LC50s and whole-body Na loss in both organisms in two distinct water chemistries ie hard and soft water. Our results indicate that the biochemical bases of copper resistance can be deeply different among yeast species.
The mean copper tolerance of plants from the mine waste was found to be four times higher than that of plants in the surrounding area. A Explain how natural selection could produce a copper-tolerant population in the mine waste. Copper Cu is an essential micronutrient for plants and has multiple functions in plant metabolic processes Hänsch and Mendel 2009 Mahalingam and Fedoroff 2003However excess Cu or contamination resulting from some human activities can result in oxidative stress in plant tissues mediated by the overproduction of reactive oxygen.
To demonstrate that the survivor capacity of C. A series of grasslands of different ages which have suffered copper pollution for different lengths of time have been used to follow the evolution of metal tolerance. Dard deviations were associated with the tolerance indices a general problem with tolerance indices and no statistically significant differences occurred among populations.
Against this background we here compare plasticity in stress tolerance in 3 copper butterfly species which differ arguably in their vulnerability to climate change. For both species the copper binding sites at the gill. For both species the.
For both species the copper binding sites at the gill. Article CAS Google Scholar. We explicitly compared acute toxicity median lethal concentrations via 96-h LC50s and whole-body Na loss in both organisms in two distinct water chemistries ie hard and soft water.
Two species that are different in their copper sensitivity are the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and yellow perch Perca flavescens. If the two species A. Some biologists have suggested that up to six of these subspecies should be classified as different species.
By contrast Poa trivialis Lolium perenne Arrhenatherum elatius and Cynosurus. Up to 10 cash back This may explain the decline in serum Na and Cl. Copper-tolerant Agrostis Tenuis plants flower at a different time from those which are not Copper-tolerant.
Species diversity in the. Protonemal growth curves for the seven popu-. At harvest plant fresh weight was assessed and a species-dependent effect of both the pH and the different Cu levels was observed Cucumber plants grown at pH 45 presented a decreasing shoot and root growth with increasing Cu concentration Fig.
The genetic basis of species differences in plants. An evaluation of sodium loss and gill metal binding properties in rainbow trout and yellow perch to explain species differences in copper tolerance. Two species that are different in their copper sensitivity are the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and yellow perch Perca flavescens.
We explicitly compared acute toxicity median lethal concentrations via 96-h LC50s and whole-body Na loss in both organisms in two distinct water chemistries ie hard and soft water. Env Toxicol Chem 2221592166. Pullulans isolates are tolerant to 0413 g CuL while no isolates of other species are able to grow at 0413 g CuL.
Use information from the passage in your answer.
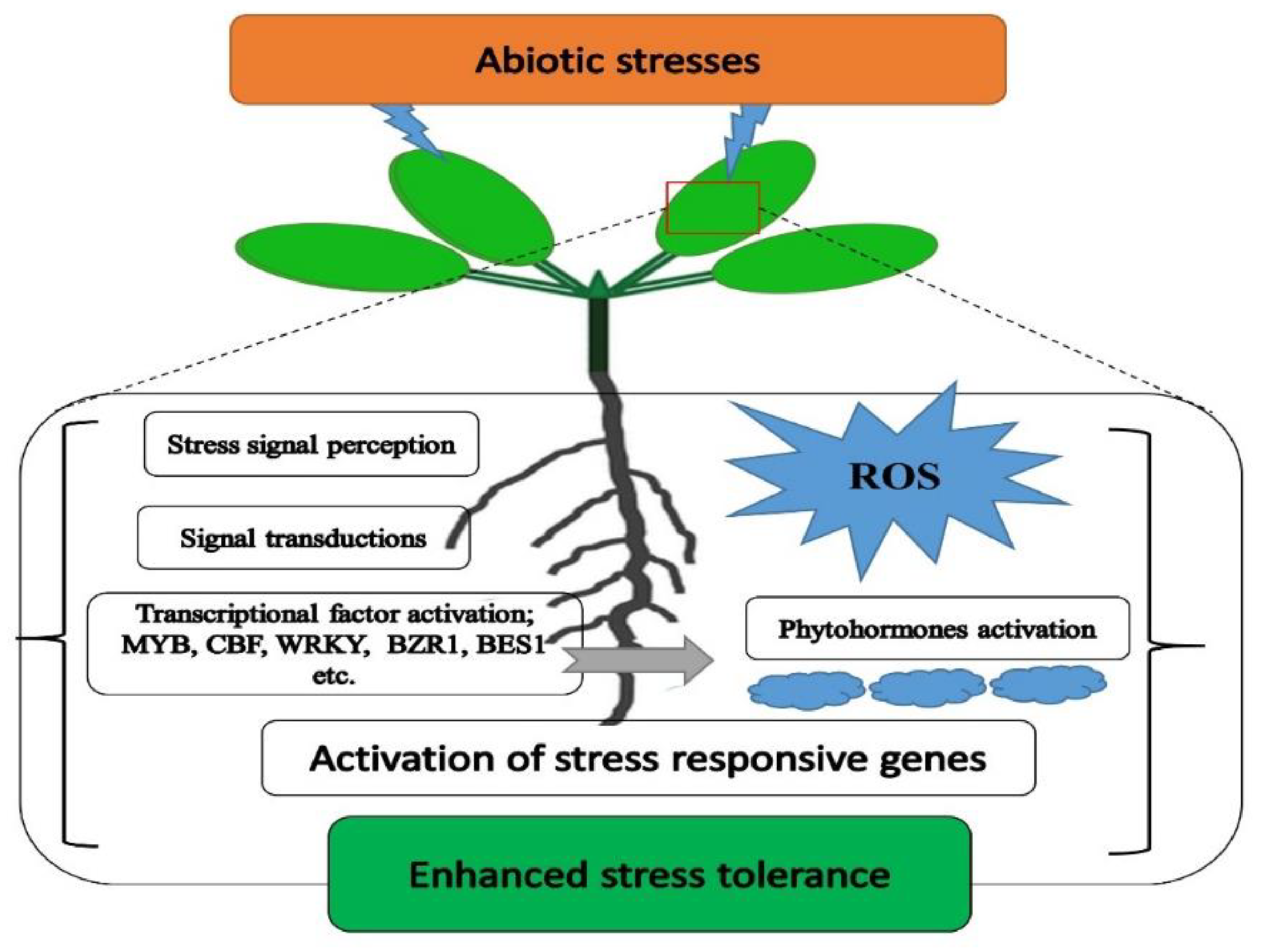
Ijms Free Full Text Transgenic Breeding Approaches For Improving Abiotic Stress Tolerance Recent Progress And Future Perspectives Html

This Is A Range Of Tolerance Graph Range Of Tolerance Is A Range Of Chemical And Physical Conditions That Biology Resources Teaching Science Secondary Science
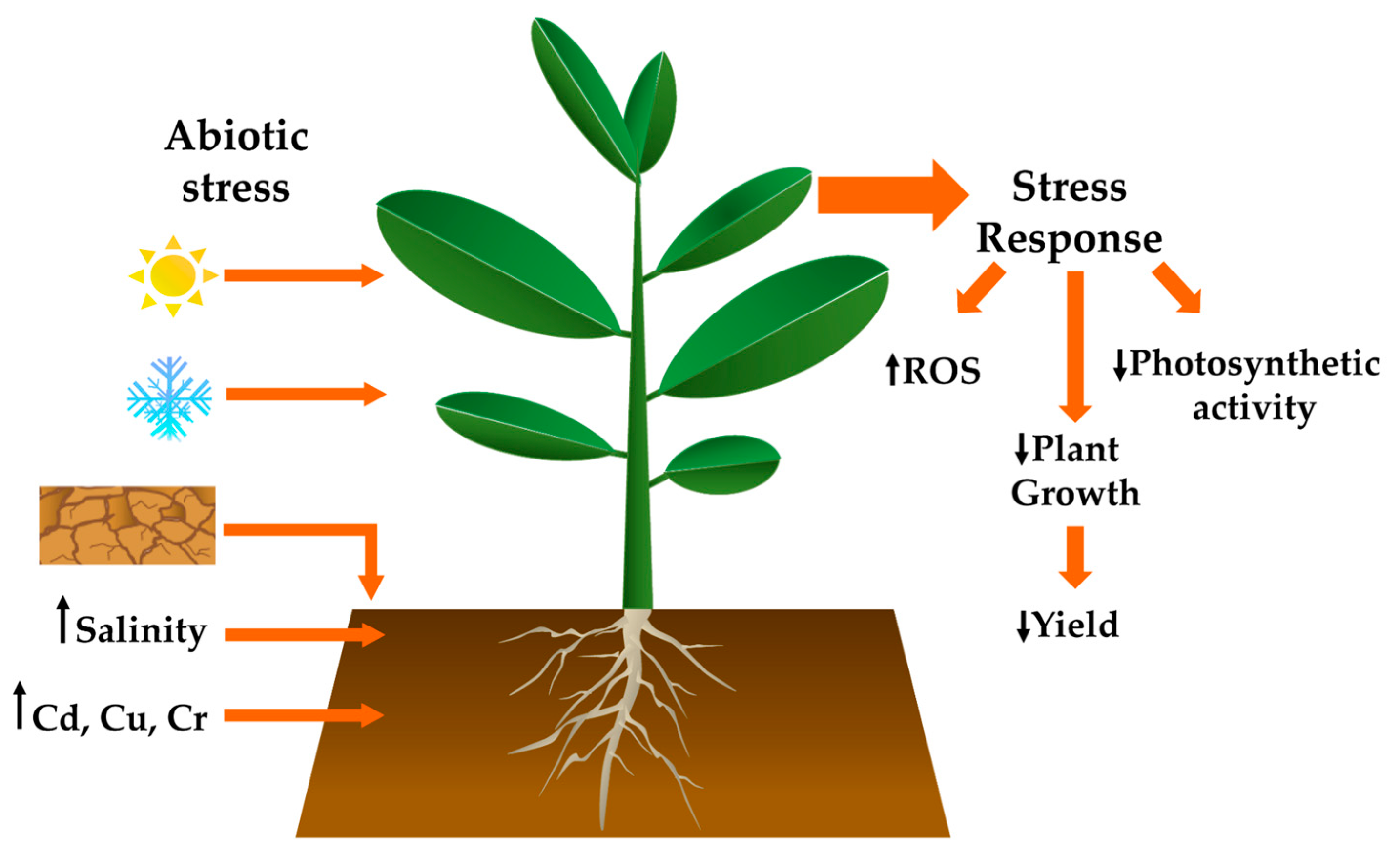
Plants Free Full Text Abiotic Stress In Crop Species Improving Tolerance By Applying Plant Metabolites Html

0 Comments